Region quadtrees in Go
Region quadtrees and efficient neighbour finding techniques in Go
Go-rquad proposes various implementations of region quadtrees.
A region quadtree is a special kind of quadtree that recursively subdivides a 2 dimensional space into 4 smaller and generally equal rectangular regions, until the wanted quadtree resolution has been reached, or no further subdivisions can be performed.
Region quadtrees can be used for image processing; in this case a leaf node represents a rectangular region of an image in which all colors are equal or the color difference is under a given threshold.
Region quadtrees may also be used to represent data fields with variable resolution. For example, the temperatures in an area may be stored as a quadtree where each leaf node stores the average temperature over the subregion it represents.
In this package, quadtrees implement the imgscan.Scanner interface, this provides a way to scan (i.e extract) the pixels in order to perform the subdivisions.
API Overview
Node interface
type Node interface {
Parent() Node
Child(Quadrant) Node
Bounds() image.Rectangle
Color() Color
Location() Quadrant
}
Quadtree interface
A Quadtree represents a hierarchical collection of Nodes, its API is simple: access to the root Node and a way to iterate over all the leaves.
type Quadtree interface {
ForEachLeaf(Color, func(Node))
Root() Node
}
Functions
Locate returns the leaf node of q that contains pt, or nil if q doesn't contain pt.
func Locate(q Quadtree, pt image.Point) Node
ForEachNeighbour calls fn for each neighbour of n.
func ForEachNeighbour(n Node, fn func(Node))
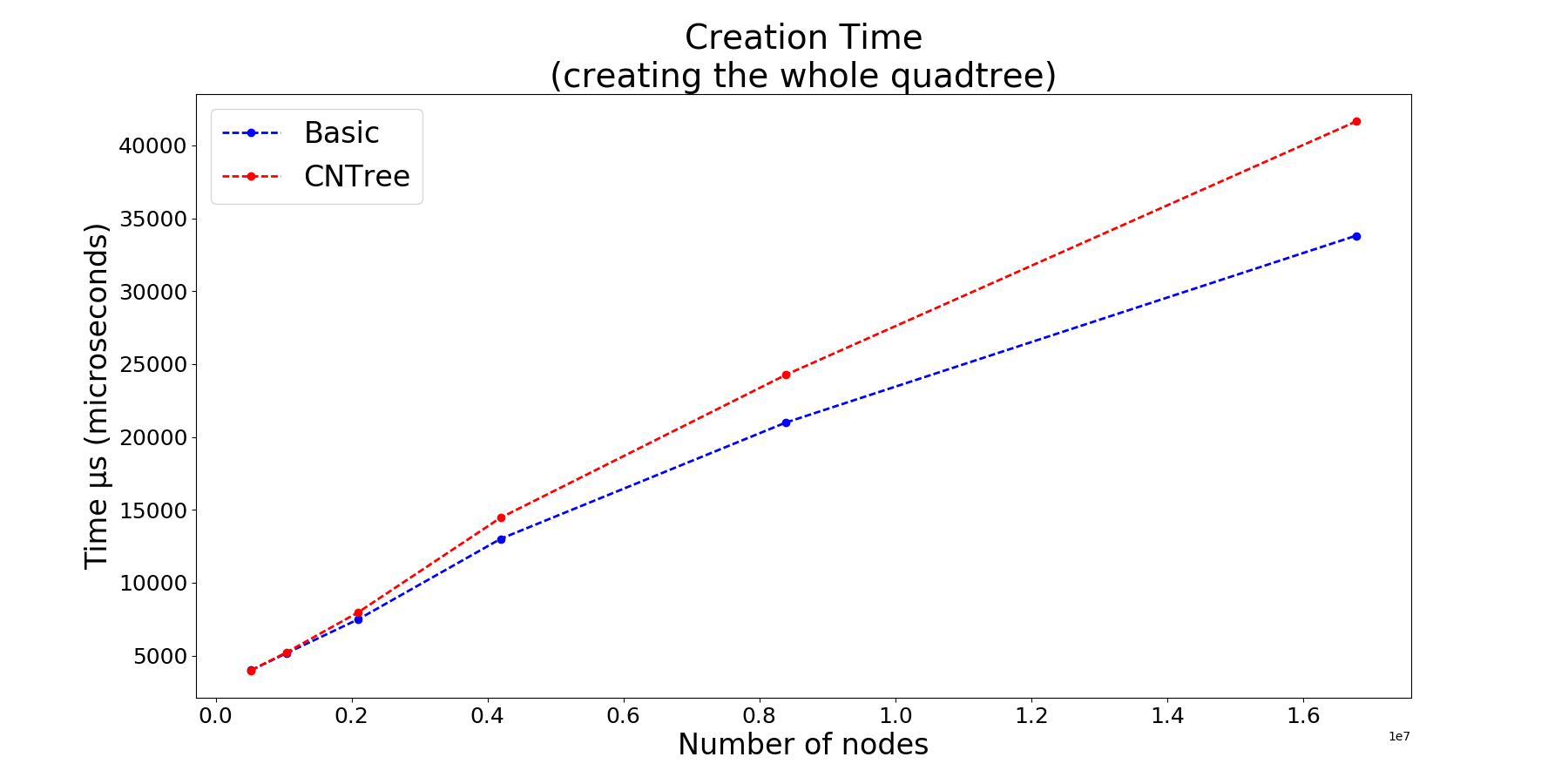
Basic implementation: BasicTree and basicNode
BasicTree is in many ways the standard implementation of Quadtree, it just does the job.
State of the art implementation: CNTree and CNNode
CNTree or Cardinal Neighbour Quadtree implements state of the art techniques:
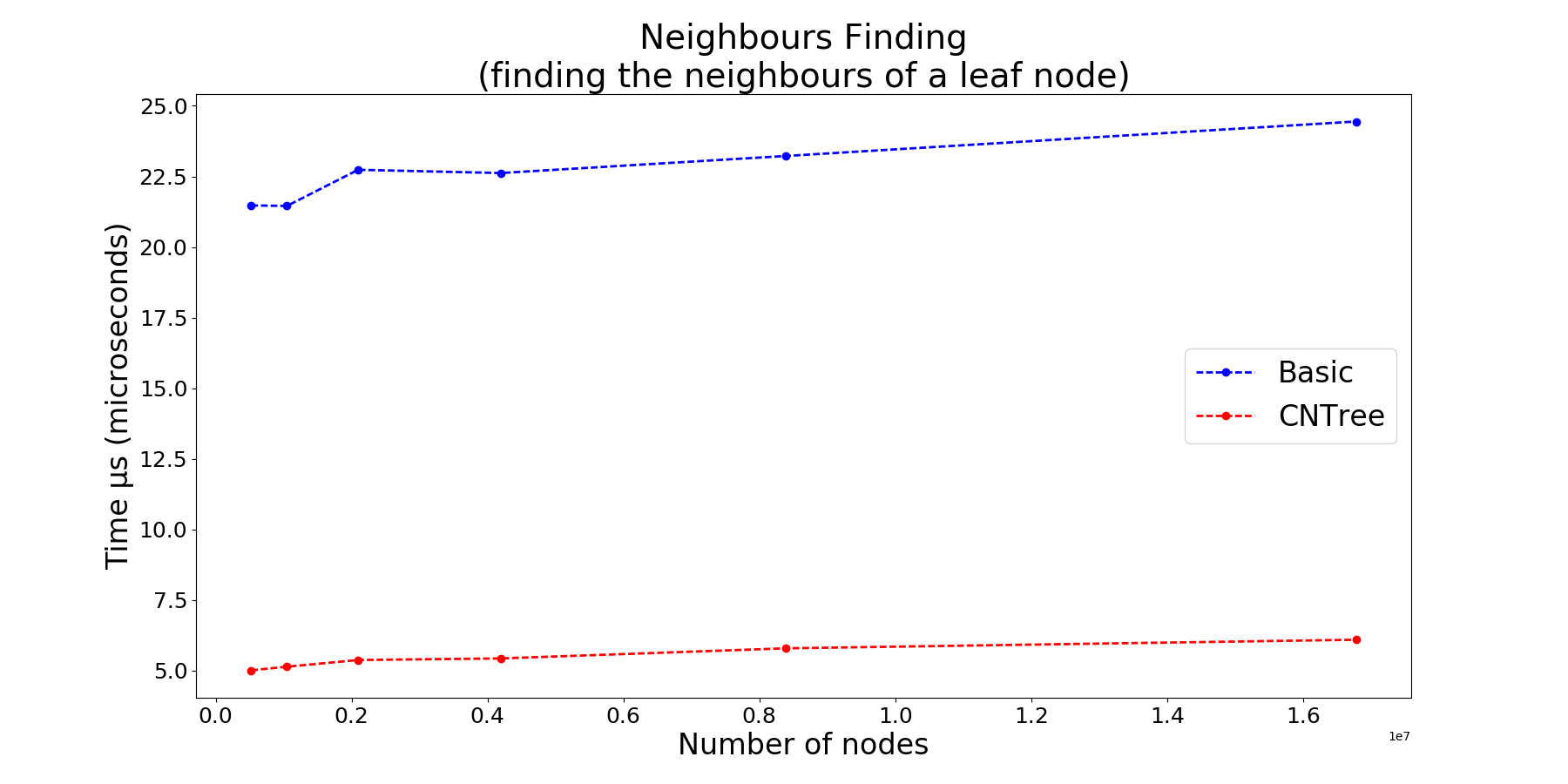
- from any given leaf node, its neighbours (of any size) are accessed in constant time 0(1) as they implement the Cardinal Neighbour Quadtree technique (cf Safwan Qasem 2015). The time complexity reduction is obtained through the addition of only four pointers per leaf node in the quadtree.
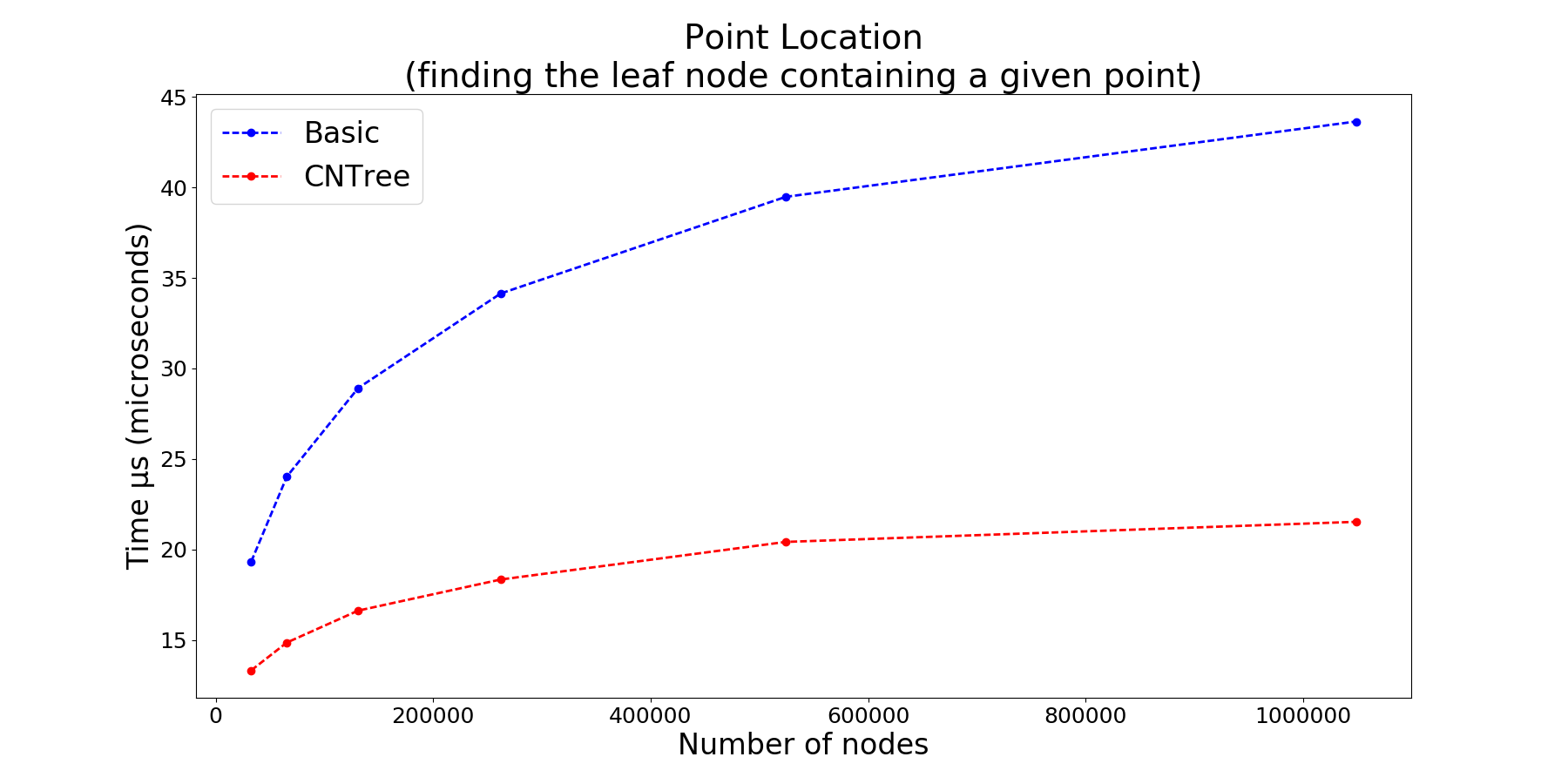
- fast point location queries (locating which leaf node contains a specific point), thanks to the binary branching method (cf Frisken Perry 2002). This simple and efficient method is nonrecursive, table free, and reduces the number of comparisons with poor predictive behavior, that are otherwise required with the standard method.
Benchmarks
Research papers
-
Bottom-up neighour finding technique. cf Hanan Samet 1981,
Neighbor Finding Techniques for Images Represented by Quadtrees, paper -
Cardinal Neighbor Quadtree. cf Safwan Qasem 2015,
Cardinal Neighbor Quadtree: a New Quadtree-based Structure for Constant-Time Neighbor Finding, paper -
Fast point location using binary branching method. cf Frisken, Perry 2002
Simple and Efficient Traversal Methods for Quadtrees and Octrees, paper
License
go-rquad is open source software distributed in accordance with the MIT License, which says:
Copyright (c) 2016 Aurélien Rainone
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.